• Splits up responsibilities for handling user interactions in an application into three layers:
–
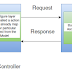
Model, View, Controller
Model
–
holds application data and business logic
–
is absolutely independent from the UIs
View
–
presentation
of parts of the Model to the user
–
independent
from the internal implementation of the Model
–
there
can be different Views presenting the same Model data
Controller
–
“bridge”
between Model and View
–
controls
the flow of the application
•
receives/interprets
user input
•
performs
operations on the Model
•
triggers
View update
Benefits:
–
better
maintainability and testability of applications
–
ability
to easily develop different kinds of UIs (e.g. console, GUI, …)
–
separation
of different tasks in development
–
code
reusability
Previous Next





0 comments:
Post a Comment